
Have you ever noticed a padlock with an https prefix on the URL(Uniform Resource Locator) bar?
Table of Contents
What is an SSL certificate?
SSL certificate stands for Secure Socket Layer. It is an encryption technology that creates an encrypted connection between your web browser and the web server or a website you’re visiting. It allows you to transmit private information without being eavesdropped or data tampering.
With the help of SSL, our sensitive information is transmitted across the world’s computer networks. The SSL certificate is essential even though a website doesn’t handle or transact the sensitive information like Credit Card details, etc., as it provides privacy, critical security, and data integrity for both the client and the server. Some of the common reason to use SSL certificate is as follows:
- Offers protection against hackers and identity theft,
- Increases the financial transactions online,
- Increases credibility and customer trust,
- SEO boost
History of SSL certificate
The SSL 1.0 which is developed by Netscape during the 1990s and it wasn’t released and published as it has a serious security flaw. Later in February 1995, they released the SSL 2.0 which also had multiple security flaws and it tends to release the SSL 3.0. SSL 3.0 is a complete redesign of the protocol.
There’s an upgraded version of SSL 3.0 which is known as TLS 1.0. TLS stands for Transparent Layer Security. Check below for the published year and status of the SSL/TLS:
| Protocol | Published | Status |
|---|---|---|
| SSL 1.0 | Unpublished | Unpublished |
| SSL 2.0 | 1995 | Deprecated in 2011 (RFC 6176) |
| SSL 3.0 | 1996 | Deprecated in 2015 (RFC 7568) |
| TLS 1.0 | 1999 | Deprecation planned in 2020 |
| TLS 1.1 | 2006 | Deprecation planned in 2020 |
| TLS 1.2 | 2008 | Unplanned |
| TLS 1.3 | 2018 | Unplanned |
Source: Wikipedia
Types of SSL certificates
- Domain Validated certificate (DV),
- Wildcard SSL certificate
- Multi-domain SSL certificate
- Unified communication certificates
- Organization Validated certificate (OV),
- Extended Validation certificate (EV).
Domain Validated certificate (DV)
Domain Validated SSL certificates otherwise known as single-domain SSL have the least assurance and basic encryption. It is typically useful for blogs and informational websites. The process to get the DV certificates are quite easy and barely anyone can get a DV certificate. Even some provide the DV certificates for free. Check out sslforfree.com. This SSL will be issued only for one main domain. If you want the SSL to be applied to your sub-domain, you should buy a new SSL certificate again or you have to buy a wildcard SSL.
Wildcard SSL
The wildcard SSL is used to secure both the main domain with an unlimited number of sub-domains simultaneously. And the wildcard SSL is much cheaper than buying n number of single domain SSL if you have many domains. This type of certificates can secure one main domain and unlimited sub-domains of the main domain. It cannot secure sub-domains of other main domain.
Multi-domain SSL
The multidomain SSL can be used as a wildcard SSL as well as to secure more than one domains with a single SSL certificate issued. In multi-domain SSL, you have the control of the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field to add, change, and delete any of the SANs as needed. A Multi-domain SSL can be a DV/OV/EV/Wildcard SSL.
Unified Communication Certificates
Unified Communications Certificates (UCC) are also considered Multi-domain SSL certificates. UCCs were originally designed to secure Microsoft Exchange and Live Communications servers. Today, these certificates can be used by website owners. This type of SSL certificate allows multiple domain names to be secured on a single certificate. UCC Certificates are organizationally validated and display a padlock on a browser. UCCs can be used as EV SSL certificates to give website visitors the highest assurance through the green address bar.
Organization Validated certificate (OV)
The main purpose of the Organization Validated certificates are assumed to be more secure as its main purpose is to secure the user’s sensitive information. To get an OV certificate, the website owner might have to complete a substantial validation process. A Certification Authority (CA) will investigate the website owner to see if they have the right to their specific domain names. This is the second precious SSL certificate.
Extended Validation certificate (EV)
The EV certificate is the most precious and highly secured certificate among all. On installing the EV certificate, the browser will display a padlock and https along with the name of the business and the country. See the example below:
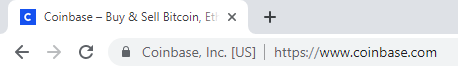
To receive this SSL certificate, the website owner will need to go through a standardized identity verification process to confirm the website owner is authorized legally to the exclusive rights to their domain. EV SSL certificates are used, in high profile websites, for applications that require identity assurance such as collecting data, processing logins or online payments.
Do we miss any information? Please share your thoughts on the comment section.
Also read: What is TOR browser? and How to use it?






Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!